What Is Amharic? – Origin, Speakers, And Similarities To Other Languages
Amharic is the national language of Ethiopia, an East African country located in the Horn of Africa – an area of the continent that juts out into the Arabian Sea. It is also the second-most spoken Semitic language in the world, after Arabic.
This fascinating language has a long and complex history, being one of the oldest continuously-spoken languages in the world.
In this article, we’ll explore the origins of Amharic, where it’s spoken, and by whom, plus discover some of the languages that are similar to it. By the end, you’ll have a much better understanding of this unique language.
Where did Amharic come from?
Amharic (or Amarigna, as it’s called by natives) is a South Semitic language that originated in the Aksumite Kingdom – an area that was once called “South Arabia” but is now Eritrea and northern Ethiopia.
Amharic is believed by many to have developed from Ge’ez, an ancient, now extinct language that originated in Arabia. Scholars say that Ge’ez-speaking Semites moved into Abyssinia (the old name for Ethiopia), naturally bringing their language with them, and this is how Amharic came to be. There is, however, still some debate on this.
Another school of thought as to Amharic’s origin is that it, being from the Southern Ethiopic group of the Semitic languages, descended from another ancient Semitic language spoken in South Abyssinia – a language similar to Ge’ez, but not Ge’ez itself.
No one can say for certain whether Amharic is a descendant of Ge’ez, though there is evidence that it was at least heavily influenced by it. Amharic also uses a slightly modified version of the Ge’ez writing system.
How old is Amharic? Is it an ancient language?
What is certain, however, is that Amharic is an ancient language. How old, exactly, is still unknown, but we know that it was first spoken at least 2,000 years ago, making it one of the oldest living languages in the world.
It came to prominence in the 12th century, as the Aksumite Kingdom began to grow in power and influence. During this time, the language spread throughout the area (now Ethiopia, Eritrea, and Sudan), as the kingdom continued to expand its territory.
The once-dominant Ge’ez language began to decline in popularity, particularly in things like literature; and by the sixteenth century, Amharic had replaced it as the lingua franca of Ethiopia, where it stands today.
Is Amharic older than Tigrinya?
There’s no certain answer to this. The origins of Tigrinya (the language spoken in Eritrea and northern Ethiopia), like Amharic, are uncertain and highly disputed.
Both languages seem to have developed independently around the same time, likely having derived from a common ancestor – either Ge’ez or another ancient Semitic language that was being spoken in the area over 2000 years ago.
This can be likened to the development of, say, Italian and French, both of which came from Latin, and are roughly the same age.
Is Amharic older than Oromo?
Again, this is difficult to say for certain. Oromo is another language spoken in Ethiopia (among other countries), and it too has ancient roots.
Oromo likely predates Amharic for the simple fact that Amharic, as it is spoken today, is somewhat of a creole language – meaning that it, like English, is a blend of two or more other languages.
Though Amharic’s origins are ancient, it no longer resembles the language whence it came, having been heavily influenced by other languages over the centuries.
Whereas Oromo, a Cushitic language, has not received nearly as much outside influence, and so retains many of its original features.
Is Amharic older than Arabic?
Yes, Amharic is older than Arabic.
Though the exact origins of Arabic are unknown, it is generally agreed that it developed from one of the ancient Central Semitic languages – specifically, Proto-Arabic.
This would place the origins of Arabic somewhere around 1600 – 1800 years ago, whereas Amharic is believed to be at least 2000 years old.
Is Amharic a Semitic language?
As has been mentioned multiple times above, Amharic is indeed a Semitic language, specifically belonging to the South Semitic branch within the West Semitic subgroup.
Where is Amharic spoken?
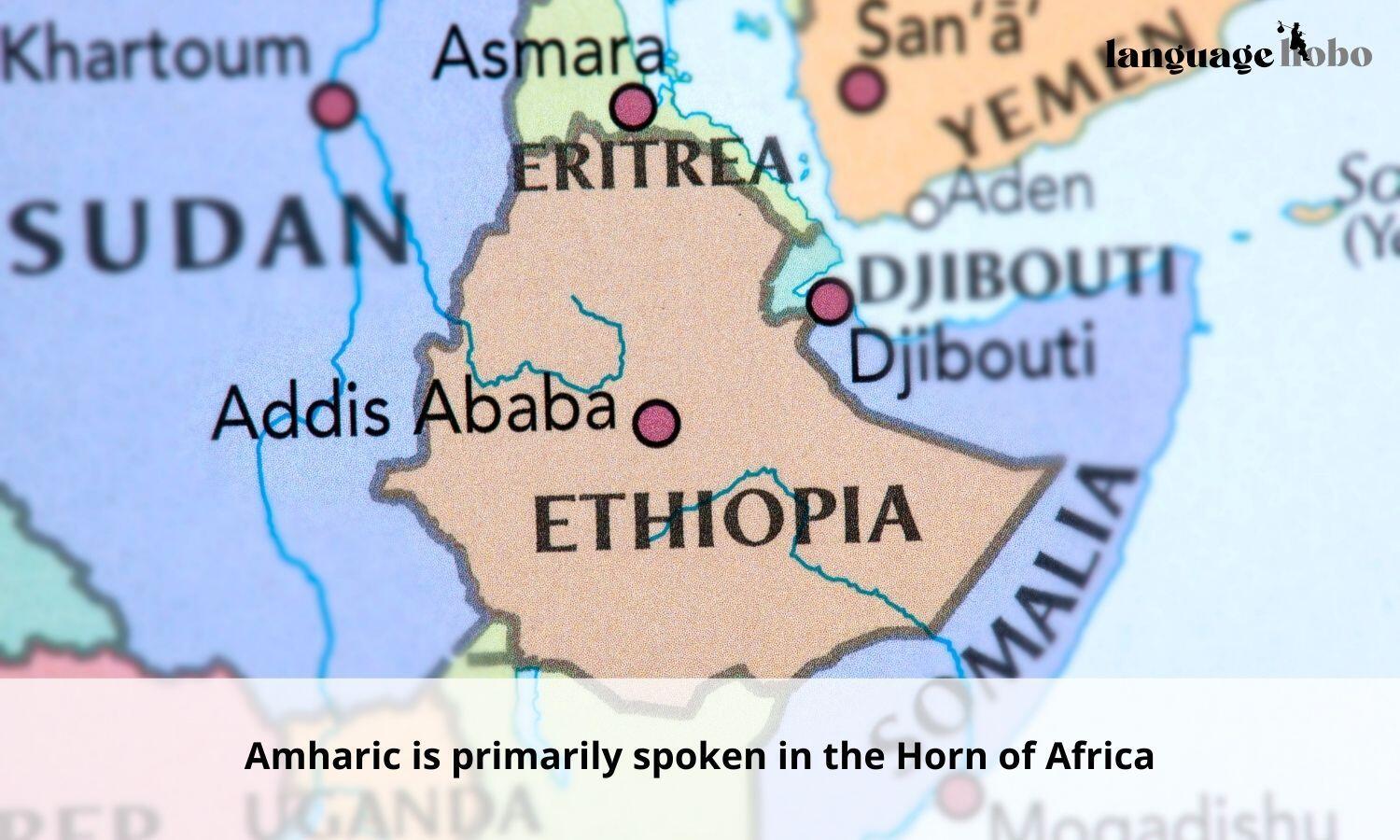
Ethiopia
Amharic is the official language of Ethiopia, where it is spoken by the majority of the population as a first or second language. Amharic is used in education, media, and government, and is spoken and understood across the country, particularly in the capital city of Addis Ababa, as well as Dire Dawa and Harar.
Is Amharic spoken in Eritrea?
In addition to Ethiopia, Amharic is also spoken in Eritrea, particularly in the city of Assab, where Ethiopians make up the vast majority of the population there.
Ethiopia and Eritrea are neighbors, and there is a long history of movement between the two, particularly during Ethiopia’s occupation of Eritrea up to 1990, which likely accounts for the spread of Amharic into Eritrea.
Israel
There is also quite a large Amharic-speaking community in Israel, made up of Ethiopian Jews (also known as Beta Israel) who have migrated there. These speakers are mostly concentrated in places like Netanya and Kiryat Malakhi.
Djibouti
Djibouti has a small but significant Amharic-speaking community, numbering over 50 thousand. They can mostly be found in the capital, Djibouti City.
Most of these speakers are Ethiopian refugees who fled the country to escape political violence and persecution, particularly during the Derg military regime (1974-1987).
Yemen
There is also a small community of Amharic speakers in Yemen, numbering around 30 thousand.
Unlike other Amharic-speaking communities in the world, however, these migrants did not intend to settle in Yemen – they were passing through on their way to more prosperous countries but ended up stranded in Yemen due to the outbreak of the Yemeni Civil War.
Egypt
Among the Ethiopians who live in Egypt, Amharic is the most used language. These speakers number around 15 thousand and are concentrated in the capital of Cairo.
These Amharic speakers, like the ones living in Djibouti, are mostly refugees who have fled Ethiopia due to political violence and instability.
Outside of Africa and the Middle East
The USA has a sizable Ethiopian community – roughly around 45 thousand, many of whom can be found in Washington DC. The vast majority speak Amharic at home.
In Canada, you’ll find Amharic speakers mainly in Ontario and Alberta.
In the UK, most Amharic speakers live in London.
Australia’s small Ethiopian-born population can mostly be found in Victoria, where Amharic is the most commonly-spoken Ethiopian language.
Who speaks the Amharic language?
The Amharic language is most closely associated with the Amhara people, who are the second-largest ethnic group in Ethiopia (after Oromo) and make up around 27% of the country’s population.
However, as the language is also the official language of Ethiopia, it is spoken by people from all ethnic groups in the country as a second language. You’ll thus find Amharic speakers among Tigrayans, Oromos, the Harari, the Gurage, and more.
These other groups tend to be multilingual, speaking not only Amharic but also their mother tongue as well as other local languages.
Do Afar people speak Amharic?
No, the Afar people – who live in Ethiopia, Eritrea, and Djibouti – speak the Afar language, which is part of the Cushitic branch of the Afroasiatic family.
This largely-nomadic group tends to self-segregate, and thus you won’t find many Afar people who speak Amharic.
How many Amharic speakers are there?
A little over 27% of the Ethiopian population (around 32 million people) speaks Amharic as a first language. When you add in second-language speakers, that number goes up to around 57 million speakers of Amharic (50% of the population). This makes Amharic the most commonly-spoken language in Ethiopia.
The Amharic-speaking diaspora is also said to number around 3 million.
What languages is Amharic similar/closest to?

Amharic is similar to some lesser-known languages spoken in Ethiopia, such as Argobba and the group of languages known as Gurage (Guragie). Those languages fall into the same South Ethiopian Semitic subgroup as Amharic.
Argobba and Amharic are mutually intelligible, which means that speakers of one language can generally understand speakers of the other language. So much so that some linguists consider Argobba to be a dialect of Amharic, not a distinct language of its own.
Gurage isn’t considered to be mutually intelligible with Amharic, though they do share many similarities. One might liken this to the relationship between Spanish and Portuguese.
Is Amharic similar to Tigrinya?
Amharic and Tigrinya are similar in that they’re both Semitic languages that likely share a common ancestor.
As one speaker of both languages said, “The root words and sentence structure between the two languages are similar, but the differences in pronunciation and writing systems (they both use different forms of the Ge’ez script) mean that they’re not mutually intelligible.“
That said, speakers of either language could generally learn the other language in a relatively short space of time.
Is Amharic similar to Oromo?
No, Amharic and Oromo are not similar languages. This is likely because they come from different language families – Amharic is Semitic while Oromo is Cushitic.
The two languages do share some words, but this is because Ethiopia has been a melting pot of cultures and ethnicities for centuries, with various groups intermarrying and borrowing words from each other’s languages.
Is Amharic similar to Arabic?
To the extent that both Amharic and Arabic are Semitic languages, they share some similarities. For instance, both languages use triconsonantal roots (i.e. words are built around three-letter roots) and share some common vocabulary, especially in the roots of the words.
Some of the words that are similar between the two languages include:
- day (Amharic: yom; Arabic: yawm)
- eye (Amharic: ayini; Arabic: ayn)
- history (Amharic: tarik; Arabic: tārīkh)
Watch this fun video to see to what extent Amharic and Arabic speakers can understand each other’s language.
That being said, while some similarities do exist, these two languages can’t really be considered “similar”, and are certainly not mutually intelligible. They have different grammatical structures, different sounds, and different writing systems. Amharic is also, unlike Arabic, written from left to right.
The other thing is that it’s unclear whether these similarities are due to a shared ancestor language or simply that these two languages have been in close contact with each other for centuries.
Is Amharic similar to Hebrew?
Hebrew belongs to the same Central Semitic subgroup of the broader West Semitic language family as Arabic, whereas Amharic belongs to the South Semitic subgroup. This means that, while there are some similarities between the two languages, they’re not closely related.
Amharic might very well have started out a lot more similar to Hebrew, but thanks to the heavy influence of Cushitic languages spoken in Ethiopia, it has acquired a lot of Cushitic vocabulary and grammatical features over the centuries.
Additionally, Hebrew, like Arabic, is written from right to left, the opposite of Amharic, as mentioned previously.
But Amharic has been influenced by Hebrew to a certain extent, particularly in the religious sphere. This is because, historically, many Ethiopian Jews used Hebrew as their liturgical language.
It is also believed that Amharic and Hebrew are more similar than Amharic and Arabic are, though this is still up for debate.
Are Amharic and Aramaic the same?
Aramaic is the (mostly) extinct language that was once spoken throughout the Middle East. So no, Amharic and Aramaic are not the same, they’re two completely different languages.
They are, however, connected in that Aramaic is yet another Semitic language, though it belongs to the Northwest Semitic subgroup – the same as Hebrew and Phoenician.
You will be able to spot cognates (i.e. words that have a common origin) between Aramaic and Amharic, as you would with any Semitic language, and several verb roots are also shared between the two languages.
Other than that, though, they’re very different, using different writing systems and writing directions (Aramaic = right-to-left), among other things.
They would have been more similar several centuries ago, but Amharic has changed a lot since then, having been influenced by non-Semitic languages.
No, Amharic is not related to Armenian. Not only do they come from completely different language families, but they’re not even spoken in the same parts of the world!
Armenian is an Indo-European language spoken mainly in Armenia and Nagorno-Karabakh (the dialect there known as Artsakh). Nowhere near Ethiopia!
Though their writing systems do look a little similar, that’s merely coincidental, as no known connection exists between the two languages.
Wrapping things up
This has probably been a lot to take in! But hopefully, you now have a better understanding of the Amharic language, its origins, and how it’s related (or not) to other languages.
Perhaps some of the information surprised you, or maybe you already knew bits and pieces. Either way, we hope you found this article interesting, informative, and not too confusing.
Now that you know a bit more about the language, why not read about the best ways to learn Amharic.
Thanks for reading!